You need to get your cross-connection control equation correct. Backflow is an inherent hydraulic problem that all public water systems can (and, at some point, will) encounter. Contamination from unprotected cross-connections or backflow incidents pose a significant risk to public health and the integrity of water systems. Backflow prevention plays a crucial role in mitigating this risk and ensuring the safety of our water supply. Typically, utilities implement a cross-connection control program to mitigate the risks–not to mention, in many states, it’s the law.
Cross-Connection Control vs. Backflow Prevention: What’s the Difference?
How We Prevent Backflow
A key component in protecting and controlling hazardous cross-connections is the utilization of backflow prevention devices, assemblies and methods such as air gaps. Across states, public water systems are required to periodically test backflow prevention assemblies. These tests require certified testers to verify the mechanisms inside the assembly function properly. Municipalities can track this information by keeping detailed testing records and following up on any failed tests to have the assembly repaired or replaced.

There are many backflow preventer test tracking software options commercially available to manage these processes digitally. Backflow software undoubtedly offers several advantages to streamline a cross-connection control program. However, it is crucial to recognize that it is only one part of the overall cross-connection control solution.
Undetected hazards, non-compliant backflow preventer installations, and unverified critical protections such as air gaps and devices can be open channels to contamination for a facility or public water system.
Backflow tests capture information often limited to:
- Pass/fail
- Make, model, and size of assembly
- Date tested and approximate location
- Tester certification
Aside from these data points, limited information regarding the condition on-site may be tracked within software. Field work, which involves physically surveying points of water usage and addressing potential backflow hazards, is an indispensable part of the solution that cannot be replaced by software.
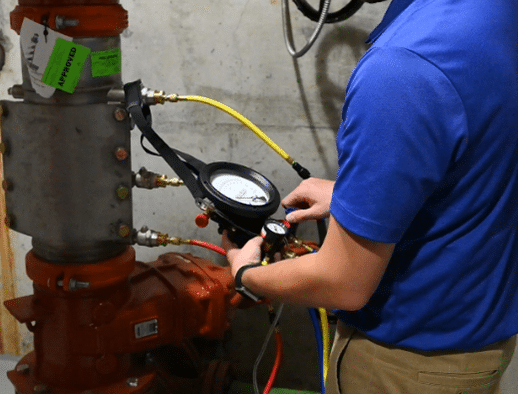
What Backflow Test Tracking Software Does
Backflow test tracking software provides numerous benefits that contribute to efficient management–and the compliance status–of water systems. Key strengths of such software can include:
- Data Management: Backflow test tracking software excels in organizing and centralizing critical information related to backflow prevention devices, inspections, test results, and compliance records. This digital approach allows for easy access to historical data, simplified record-keeping, and streamlined reporting and analysis. The software enables water system administrators to efficiently manage the vast amounts of data associated with backflow prevention.
- Automation: One of the significant benefits of this software is the potential for automation. It can streamline administrative tasks like generating reminders for inspections and tests, scheduling appointments, and sending notifications. These automations enhance efficiency, reduce the risk of oversight or missed deadlines, and help ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Automation features free up valuable time for utility staff to focus on other core responsibilities.
- Efficiency: Backflow test tracking software eliminates the need for manual paperwork, reduces time-consuming data entry, and facilitates effective communication between stakeholders, including water suppliers, technicians, and property owners. The software’s efficiency leads to faster response times, streamlined workflows, and enhanced program management.
- Sustainability: One of the significant benefits of using software is the reduction in waste. By digitizing processes and eliminating the need for physical paperwork, the software minimizes paper use. Water system administrators can manage inspections, tests, and compliance records electronically, reducing the reliance on printed documents.
What Backflow Test Tracking Software Doesn’t Do
While the benefits are real and tangible, software can’t solve all your cross-connection control problems by itself.
- Physical Examination: Field work involves physically examining points of water usage to identify potential cross-connection hazards and ensure appropriate backflow prevention measures are in place. It allows professionals to inspect plumbing systems, identify faulty devices, and assess potential risks that may not be captured through digitized data.
- Hazard Detection: Undetected backflow hazards pose significant risks to public health and water system integrity. Fieldwork provides an opportunity to proactively locate and eliminate these hazards. By conducting site visits and surveys, experts can identify potential sources of contamination–such as unprotected irrigation systems, chemical storage areas, or industrial processes–and implement appropriate preventive measures.
- Compliance: Fieldwork is instrumental in verifying the proper installation of Backflow Preventers and ensuring compliance with regulations and standards. It allows technicians identify any necessary repairs or replacements. Field inspections also provide an opportunity to educate property owners and occupants on best practices.
- Elimination of Hazards: Every water system is unique, and effective cross-connection control requires customized approaches. Fieldwork allows professionals to adapt strategies to the specific needs and complexities of each site; it enables them to make informed decisions about corrective actions, installation, and compliance based on on-site observations and expertise.
- Non-Testable Backflow Prevention: Fieldwork is essential to identify any non-testable backflow prevention (methods or devices) that cannot be adequately assessed through test tracking software. Since this type of backflow prevention isn’t testable, there will never be test data to review. In these cases, field professionals must physically examine each connection to ensure it is effectively isolated according to codes and regulations.
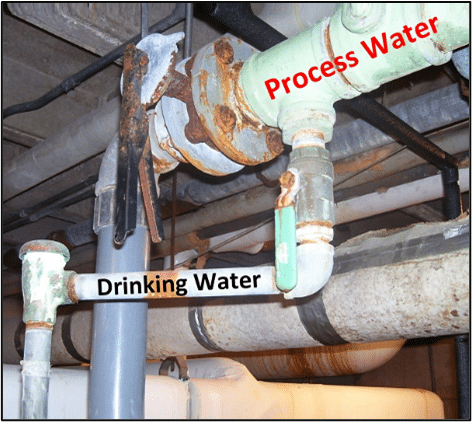
The implementation of fieldwork requires a tailored approach that aligns with the public water system’s resources, objectives, and regulatory requirements. Whether through in-house training, external inspectors, or contractor engagement, the goal is to ensure that fieldwork is integrated seamlessly, leading to effective inspections, hazard identification, and the implementation of appropriate preventive measures to protect public health and maintain the integrity of the water supply.
Next Steps for Your Utility
Software and fieldwork complement each other, and, together, the two support comprehensive and successful cross-connection control programs.
How to implement fieldwork in your cross-connection control program:
- Decide who will perform on-site survey work to identify unprotected hazards.
- Ensure the cross-connection control plan specifies compliance enforcement.
- Organize survey activities to prioritize higher hazard facilities.
- Inform water customers of their responsibility when access or corrective action is required.
The combination of software and field work creates a robust program that protects public health, ensures compliance, and maintains the integrity of our water supply. By recognizing the significance of both aspects, we can achieve comprehensive cross-connection control and mitigate potential risks effectively.


