Summary:
Manufacturers and large industrial facilities face a variety of challenges when managing complex piping systems, many of which arise not from the internal condition of the pipes, but from external factors. Below are the top ten issues, along with actionable solutions to keep your operations efficient, safe, and compliant.
4 Proven Tips to Secure Reliable Piping Schematics in Your Facility’s Budget
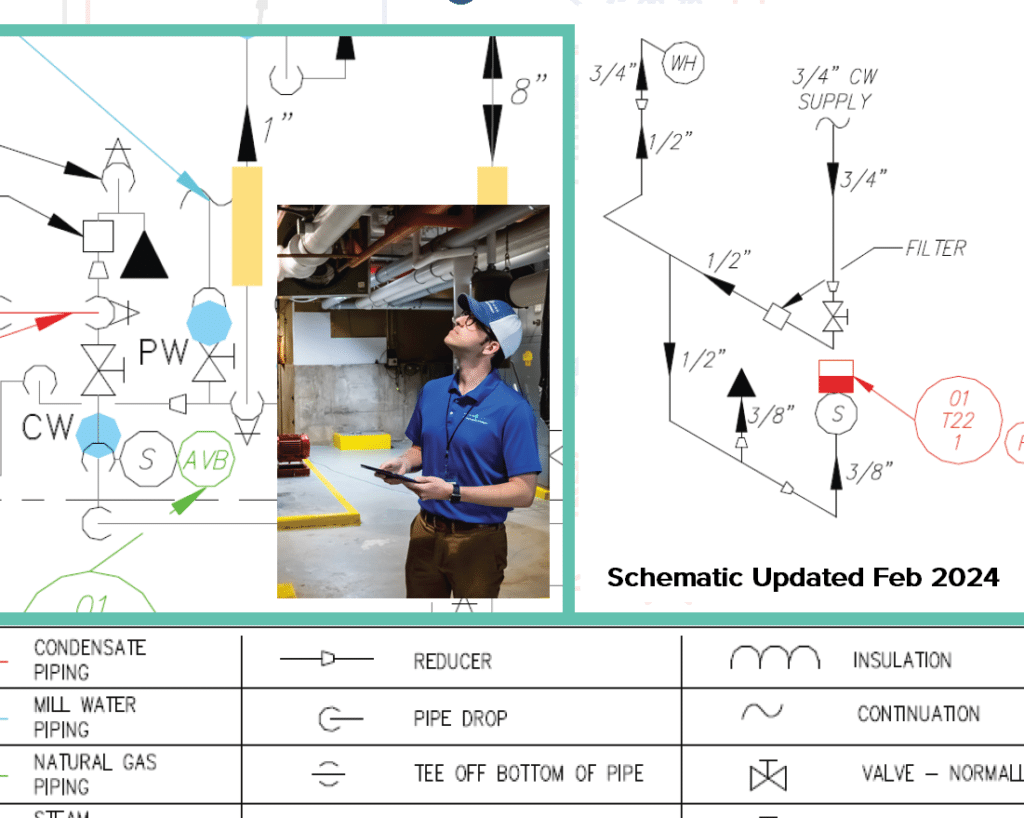
1. Inadequate Documentation and Mapping
Issue: Incomplete or missing records of piping layouts make it difficult for maintenance crews to locate components, leading to delayed repairs and inefficiencies.
Action Step: Implement a thorough mapping process using modern tools such as digital blueprints, 3D modeling, or GIS (Geographic Information System) software. Regularly update these records to ensure they reflect any changes or upgrades to the system.
2. Coordination Challenges During Repairs or Upgrades
Issue: Coordinating between departments, contractors, and utility providers during repairs or upgrades often results in downtime and operational delays.
Action Step: Establish a centralized project management system that coordinates scheduling and task delegation across all teams involved. Appoint a dedicated project manager to oversee communication and workflow, minimizing miscommunication and conflicts in scheduling.
3. Insufficient Employee Training on Piping Infrastructure
Issue: Lack of proper training on the operation, maintenance, and emergency procedures of piping systems can lead to safety risks and operational errors.
Action Step: Develop a comprehensive training program that includes regular workshops and hands-on training for employees. Create a certification process to ensure that staff are knowledgeable about system maintenance and emergency shutdown procedures.
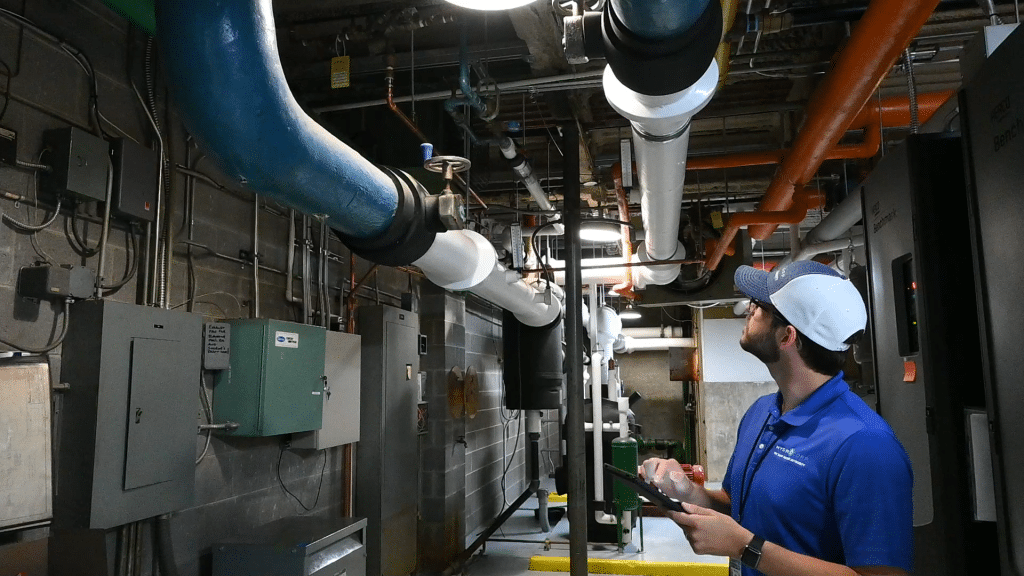
4. Difficulty Accessing Pipes
Issue: Poor accessibility to piping systems, especially in hard-to-reach areas, complicates inspections and routine maintenance.
Action Step: Conduct an access audit to identify areas where pipes are difficult to reach. Install access panels, catwalks, or specialized inspection ports where necessary to improve accessibility for maintenance and emergency repairs.
5. Regulatory Compliance and Audits
Issue: Meeting environmental, health, and safety regulations (e.g., OSHA, EPA) can be time-consuming and costly, especially if systems are not up to standard.
Action Step: Schedule regular internal compliance audits and work with regulatory experts to ensure all piping systems meet the required standards. Invest in compliance management software to track certifications, inspections, and necessary upgrades, reducing the risk of fines or shutdowns.
6. Energy Inefficiency
Issue: Poorly insulated or inefficiently designed piping systems can lead to significant energy losses, driving up operational costs.
Action Step: Conduct an energy audit to identify inefficiencies in the piping system. Upgrade insulation where needed and consider retrofitting older systems with energy-efficient piping designs or materials. Additionally, installing variable-speed pumps can optimize energy use.
7. Third-Party Vendor Delays
Issue: Dependency on external vendors for parts, repairs, or upgrades can result in supply chain disruptions, causing delays in critical system repairs.
Action Step: Build relationships with multiple vendors to create redundancies in the supply chain. Keep an inventory of high-demand parts on-site to minimize delays caused by shipping. Consider implementing a vendor performance tracking system to monitor reliability and adjust partnerships accordingly.
8. Water Supply and Resource Limitations
Issue: Fluctuations in water quality, pressure, or availability from municipal or private utilities can disrupt operations, particularly in regions facing water scarcity.
Action Step: Install backup water storage or on-site water treatment systems to ensure consistent supply. Monitor water usage closely and implement water conservation practices, such as recycling water in non-potable processes, to reduce dependency on external sources.
9. Communication Breakdown Between Teams
Issue: Miscommunication between facility managers, maintenance staff, and external contractors can result in misaligned priorities and extended downtimes during repairs or upgrades.
Action Step: Implement a unified communication platform, such as a cloud-based project management tool, that allows real-time collaboration and tracking of ongoing tasks. Schedule regular meetings to align priorities and ensure that all teams are informed of system status and upcoming changes.
10. Fast Access to Shutoff Valves During Emergencies
Issue: Lack of quick access to critical shutoff valves during breakdowns or emergencies can escalate system failures, leading to extensive damage or safety hazards.
Action Step: Conduct an audit of shutoff valve locations and install additional easy-access shutoff points where necessary. Clearly label all valves and ensure their locations are highlighted in updated system schematics. Provide training for staff to quickly locate and operate shutoff valves in case of an emergency.
Recap
By addressing these external challenges proactively, manufacturers can improve the reliability, efficiency, and safety of their piping systems. Implementing these action steps will reduce downtime, enhance compliance, and optimize energy and resource use across the facility.


