Summary
Key Points & Takeaways:
- Water quality is a crucial issue for industrial and manufacturing facility managers for health, safety, and regulatory compliance.
- Cross-Connection Control Surveys, which are a thorough surveying of all potable water piping infrastructure, can pinpoint interconnections that could allow pollutants or contaminants to enter the facility’s potable water system.
- Maintaining and regularly updating Facility Piping Schematics with rigorous mapping and documentation allows managers to have access to accurate and up-to-date information on their system and valve locations.
Water plays a critical role in industrial and manufacturing facility operations, utilized in processes ranging from machine tooling to food and beverage manufacturing. This reliance on water comes with the responsibility to ensure its purity, safety, and separation from contaminants. Industrial and Manufacturing Facility Managers have a crucial need to closely monitor their piping systems to prevent the contamination of their water supply to keep their employees and customers safe. Two essential tools that can help keep water shielded from the dangers of backflow contamination and legionella outbreaks are:
- Cross-Connection Control Surveys: The thorough surveying of all potable water piping infrastructure in a given facility.
- Facility Piping Schematics: Maintaining and regularly updating piping schematics that are aligned with maintenance activities.
Water Quality
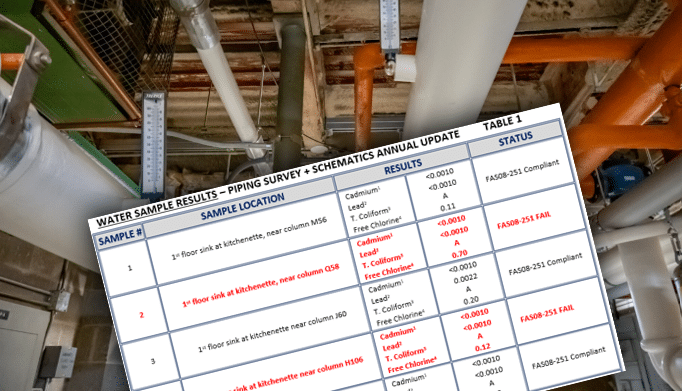
In industries where potable water is a primary ingredient in the final product or used in the manufacturing processes, maintaining its quality is paramount. The safety of onsite employees and the integrity of products, especially in consumable goods manufacturing, hinge on the assurance of a clean and safe water supply. A worst-case scenario could even see a backflow incident at one facility spreading throughout the public distribution system and affecting the public water supply.
Identifying the Risks
Undetected cross-connections pose a threat when backflow occurs and routine action is not utilized to eliminate them. Backflow is an inherent problem in any hydraulic system that occurs when a drop or change in the system’s pressure causes the normal flow of water to be reversed, potentially allowing contaminants to enter the potable water system. This poses a dual threat—compromising the safety of the water consumed by employees onsite and affecting the quality of water used in manufacturing processes, particularly in the production of consumable goods.
Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory bodies such as OSHA have established codes and requirements for industrial facilities. Compliance with these regulations is not only a legal obligation but also a moral responsibility to ensure the health and well-being of the workforce and consumers. Understanding and adhering to regulatory measures is fundamental in maintaining the safety of water in industrial processes. Maintaining safe drinking water for employees, visitors and processes is not only an OSHA requirement, it’s a moral obligation of any facility owner/operator.
Cross-Connection Control Surveys/Inspections
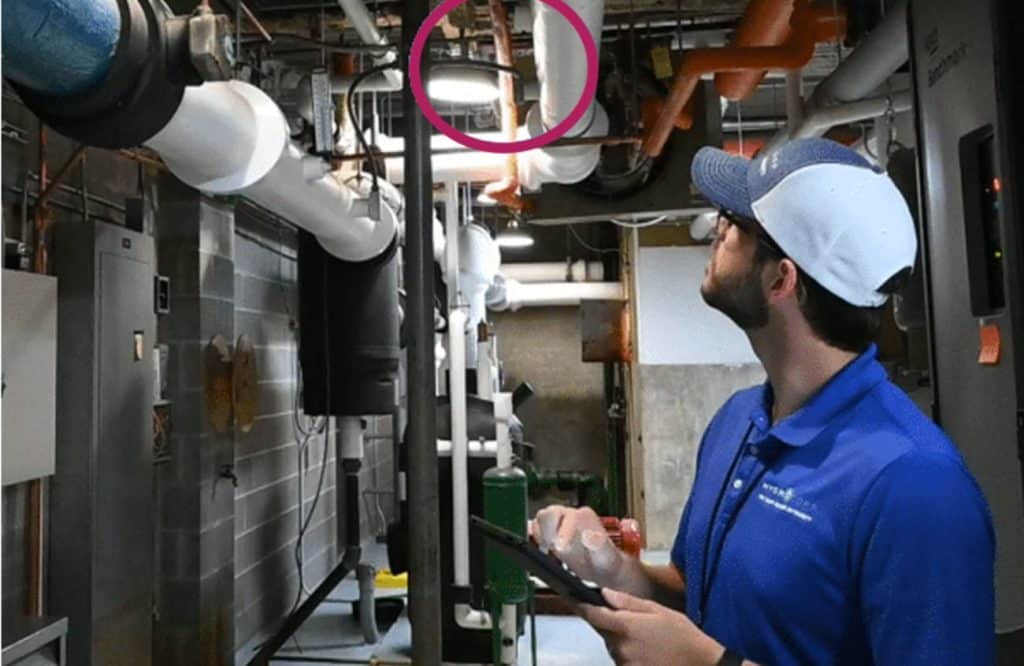
One of the primary tools in preventing water contamination is conducting onsite Cross-Connection Control Surveys. These surveys focus on identifying and eliminating actual or potential cross-connections where the potable water may come into contact with non-potable sources under backflow conditions. Rigorous and routine inspections of the piping system and the points of use of water throughout the facility will help pinpoint potential vulnerabilities in the system, allowing for proactive measures to be taken to safeguard water quality. These measures could include installing a backflow preventer, eliminating the connection, or reconfiguring the problematic piping arrangement.

By addressing cross-connections, industrial facilities can prevent the unintentional flow of contaminants into their potable water systems. Cross-Connection Control Surveys serve as a proactive defense mechanism, mitigating risks before they can compromise the safety of the water supply.
Updated Piping Schematics/Mapping
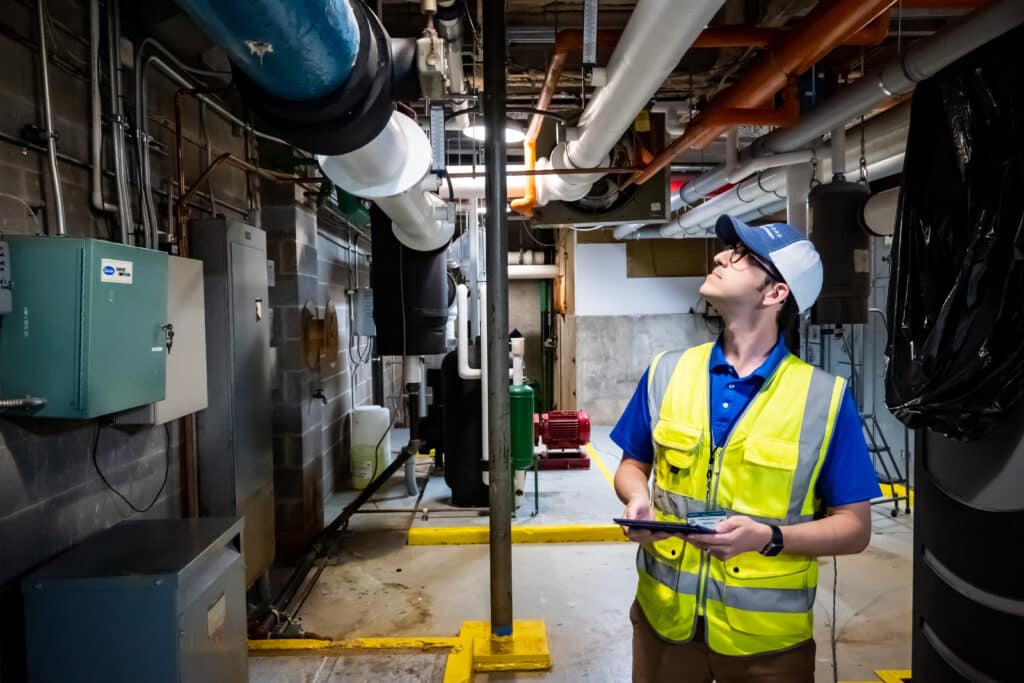
Accurate and up-to-date piping schematics play an equally vital role in water safety. These schematics provide a comprehensive visual representation of the facility’s piping system, aiding in the identification of potential cross-connections and facilitating efficient maintenance.
Regular updates to piping schematics ensure that facility managers and maintenance personnel have correct and current information at their disposal. This is crucial for responding promptly to any emergencies within the system. If accurate information about valve locations is not immediately available, leaks, flooding, or other issues could go on for hours. Regularly updating piping schematics will also uncover any dead leg piping in the system, where the potential for a legionella outbreak is incredibly high.
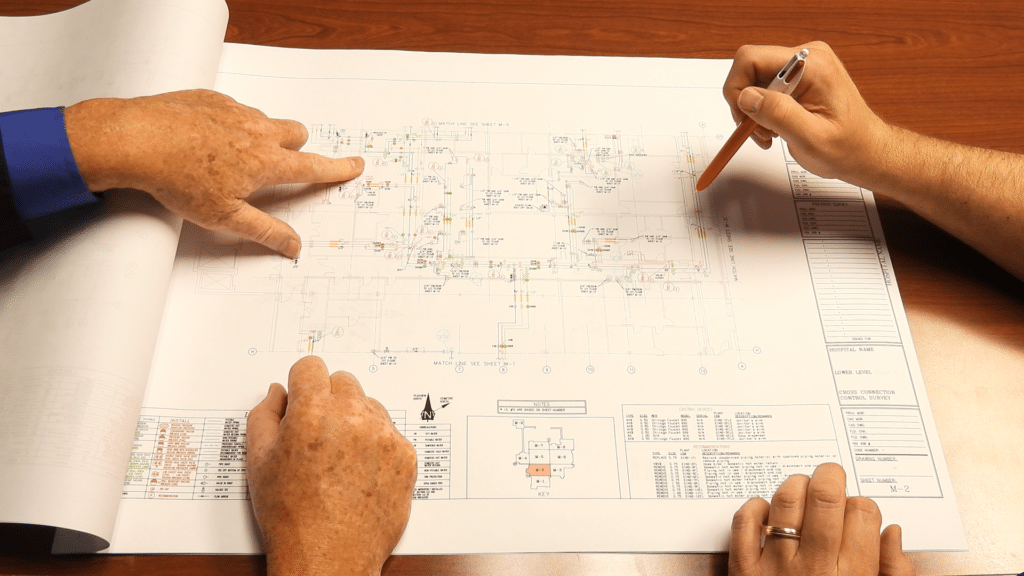
While many technologies have become available, such as digital scanning, there is currently only one way to get piping schematics updated with current “as-is” conditions: that is the meticulous method of visually tracing every inch of piping in a specific system; from its initial source, up through ceilings and walls, to each end point use. This means: climbing ladders, inventorying all related valves, labels, and connections, and rendering field drawings of the piping system being surveyed.
Conclusion
Industrial and manufacturing facilities must prioritize the safety of their water piping system. The potential consequences of water contamination extend beyond regulatory penalties; a backflow event could negatively impact the health of employees, the quality of products, and potentially threaten the safety of the public water supply. Cross-Connection Control Surveys and Accurate, Up-To-Date Piping Schematics are two indispensable and complementary tools, offering a multi-pronged and proactive defense against potential water contamination events. By embracing these measures, industrial facility managers not only fulfill their regulatory obligations but also build a safer, healthier, and more sustainable industrial landscape.

